With regard to employment in electronics manufacturing assembly, SMT or Surface Mount Technology has remained as one of the transformations in the circuit board assembly line. If considered from the perspective of its application from the beginning of its use up to the modern tendencies in electronics, SMT can be described rather as a perfect example of an ability to optimize during the way towards miniaturization and performance increase. This book contains tips on the tackle of Surface Mount Technologies, which covered the background of SMT, different components of the technology, the assembly processes and benefits of using this technology, the application used in the electronics industry, and the future of SMT in electronics production.
Origins and Evolution
SMT developed in the 1960s due to the limitation of THT, this was the previously used method of inserting electronic parts on the printed circuits. THT involved the use of a PCB where on the board there were holes made and the Leads of the component were passed through these holes and soldering was done in the back. As for the advantages and disadvantages of THT: it was space efficient but very bulky; it had a somewhat complex structure in production; concerning the electrical performance it was quite good.
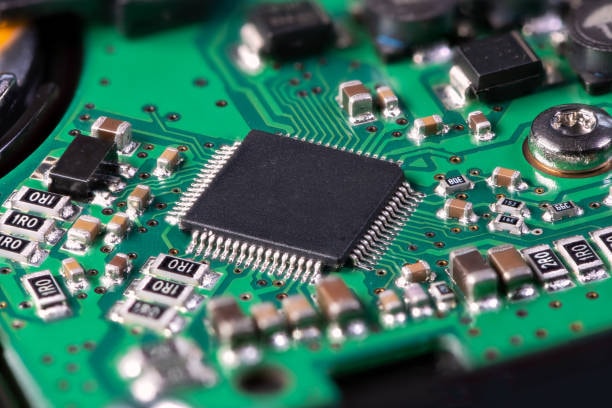
SMT processed and delivered components with the leads minimized to smaller sizes or no leads at all and soldered onto the board’s surface. This movement assisted in doing away with the need for holes drilling and enabled the creation of an environment for carrying out automation assembly operations which in turn assisted in the enhancement of electronics manufacture business.
What is surface mount technology?
Surface mount vs through hole technology differences? Surface MountTechnology (SMT) refers to joining of electronic elements on the surface of the PCB with no usage of through-hole connections. This is especially so as we shift from Through-Hole Technology (THT) that is our component leads are inserted through holes made on the PCB and soldered at the other end. Applying SMT it is established that parts are generally much smaller in this material that leads to increase in components density and product miniaturization. SMT assembly involves the use of automatic tools to place the component parts in their required position on the PMC then fix them by soldering. In electronics manufacturing it has been applied in smoothening of the devices, making them compact, better dielectrics and fabrication of the products hence leading to miniaturization of electronics goods.
Key Components in SMT
- Surface Mount Components: There are resistors , capacitors, diodes, transistors and integrated circuits (ICs) and other active & passive surface mount devices.
- Printed Circuit Boards (PCBs): SMT utilizes PCBs that will incorporate pads and traces that are specifically meant for surface mount devices. Such PCBs are normally manufactured from material such as FR-4 offering adequate electrical insulation and mechanical support.
- Solder Paste: Solder paste: a key component in SMT assembly and somewhat similar to the concept of paste, solders contains small balls of solder in a flux medium. It is used on the pads of the PCB prior to component insertion.
- Pick-and-Place Machines: These robotic pick and place machines accurately select the surface mount parts from reels or trays and deposit them on the solder paste applied lands of the PCB.
- Reflow Ovens: Following component placement, the PCB goes through the reflow ovens that cause the solder paste to reach its melting point and make firm physical and electrical contacts between the components and the PCBs..
Assembly Process
The SMT assembly process involves several key steps:
- Stenciling: Solder paste is used to print on a thin layer and it is put on the side of the PCB with pads.
- Pick-and-Place:Some parts must be picked from reels or trays with the help of picking tools according to the assembling specifications and placed at the proper solder paste location on the pads.
- Reflow Soldering: Individual PCBs with components are put through a reflow oven and solder paste melts and forms solder joints hence fixing the components firmly on the PCB.
- Inspection: AOI and the other methods are used to confirm proper soldering features, placement of components and integrity in the general assembling process.
- Cleaning and Post-Processing: Removing any of the residual flux in PCBs may also be done by other processes before going through other process like test, program, pack among others.
Advantages of Surface Mount Technology
These are the advantages of surface mount technology:
Space Efficiency
Possibility to get rather high component density on boards is one of the most striking benefits of switching on SMT. SMT has a characteristic of placing components on the surface of the pads to make compact devices that are smaller in size without compromising on the use and operation of the equipment.
Improved Electrical Performance
Component sizes used in SMT are also comparatively smaller than the ones in THT and create path lengths for electrical signals shorter; moreover, SMT has lesser parasitic capacitance and inductance trouble, better high frequency correspond. Such improvements are made for increasing the operating speed of the system and decreasing the power consumption as well as general improvement of the electronic systems.
Automation and Cost-Effectiveness
This is an advantage since SMT assembly is automated hence will mean that the product yield will be better and the costs of labor will be lesser. For this reason, throughput rates are high because pick-and-place machines, reflow ovens and automated inspection systems are used and with fee high volume pro formas every item assembled costs much less.
Multilayer PCB Compatibility
SMT comes handy where there are overlapping circuits needed to be mounted and sections with power/ground planes as well as multiple signal planes. A characteristic such as this makes it possible to introduce the newest features of the products and establish complicated electronic systems.
Thermal Management
SMT also assists in the offering of installation of heat sinks, thermal vias, and the thermal pads on the outer layer of the PCB. It has the ability to cool characteristics generated from high power elements to retain the efficiency and prolong the life span of circuits.
Applications of Surface Mount Technology
These are the applications of surface mount technology:
Consumer Electronics
SMT has revolutionized consumer electronics and has made it possible for developers to have the innovation of smart devices including; phone, tablets, laptops, and wearable gadgets. Since SMT involves a more compact equipment, more features can be incorporated in a single unit and consequently promotes the competitiveness of the Consumer Electronics manufacturers.
Automotive Electronics
In wake of the automotive market segments SMT plays an important role in the manufacturing of ECUs, Sensors, Comfort and Control Systems and ADAS. SMT is most advantageous in those vehicles where the volume of the car and its weight are of a major concern, which mainly depend on the size of the car.
Medical Devices
Medical devices require various Electronics that are placed into them and benefit from SMT due to its reliability of the process, the smaller circuits generated, and the low cost. Mobile technologies enshrined in a portable monitoring device or an implant technology for medical implants gives rise to this galaxy of innovative health care which lead to improvement of the quality of life of the affected patient and for health care diagnosis or a certain procedure to take place.
Industrial and Aerospace Applications
SMT is generally utilized where conditions relating to the operating environment are very much critical for the electronic devices and equipment, if it is an aerospace component or a defense item, industrial automation where the harsh environmental rating is highly demanding if it is avionic equipment, control panel assemblies, communication equipment etc. This is real because SMT has options like environmental isolation as well as anti-vibration to bring to the table and these are very important in markets with great and active operations.
Future Trends and Innovations in Surface Mount Technology
Miniaturization and Integration
This is just catching up to the world that is calling for smaller and versatile electronic devices. SMT is expected to introduce more miniaturization attributes to the whole picture and achieve the integration of many circuit functionalities in miniscule circuits. The above activities will spur new innovations in the technologies such as the IoT devices, Wearable technologies as well as smart structures.
Advanced Materials and Processes
Higher reliability of SMT assemblies will be achieved by enhancing productivity of fabrication of solder materials, conductive adhesive and flexible substrate. Nanomaterials and conductive inks composition are also believed to have great future to be used in the next generation SMT because of the conductivity, thermal and mechanical properties.
3D Integration and Packaging
Some of these are the three dimensional integration solutions including chip stacking as well as system-in-package also known as SiP. SMT is inherently well-aligned with 3D packaging, and later with high-performance computing, artificial intelligence, and edge computing equipment.
Green and Sustainable Manufacturing
Electronic manufacturing company: Green practices that are being implemented because of environmental factors are discussed in this paper. High performance SMT processing, which will reduce waste, energy consumption, and emissions for organizational sustainability, will also become the new standard due to the world’s rising concern on environment conservation and reducing impact of the industry.
Conclusion
SMT has been described as the technology of depositing electronic components on the surface of printed circuits boards with a view to making electronic equipment compact, improve electric characteristics and introduce the aspect of automation. Originally, SMT evolved as an addition to THT has in the recent past transformed to a standard procedure as a production method in consumer electronics, aerospace industries, among others. Concerning its advantages like spatial saving, electrical characteristics and cost, it has become practically indispensable in contemporary electronic design and manufacturing. Thus the trends for the future around SMT are miniaturization integration and sustainability and these should encourage further development of new technologies and electronics.
